When a word as Global crisis is uttered, the description of which is understood to be “food Shortage”. It occurs when rates of hunger, starvation, and malnutrition rise sharply at local, national, and global levels. The recent increase in food prices has reduced access to food for many people, particularly the poor, in a large number of developing countries. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has identified that 37 developing countries are facing immediate hunger needs, with 20 of them being least developed countries (LDCs). On average, between 50-80 percent of personal income is spent on food in these countries, contributing to poverty.
The World Food Program (WFP) estimates that more than 345 million people face high levels of food insecurity in 2023 in the 79 countries where it operates.
The question of why the food crisis is increasing every year has arisen for many years. The leading causes and drivers of food insecurity include:
Conflicts, Violence, and Wars:
Conflict remains the biggest driver of hunger, with 70% of the world’s hungry people living in areas afflicted by war and violence. The events between Ukraine and Russia further illustrate how conflicts exacerbate hunger. Additionally, a recent example is Syria’s agricultural production, which has been greatly affected by conflict. As a result, 5.5 million Syrians have suffered from food shortages.
Lack of Access to Farming Lands:
Our food productivity depends on our farming lands, as food is grown or produced from the land. If a person has access to farming land on a small scale, they will not suffer from food shortages because land ownership strengthens agricultural productivity. Lack of access to farming land means a lack of a key resource for producing food crops.
Natural Disasters:
Droughts, cyclones, floods, typhoons, hurricanes, and other natural disasters have a destructive and gigantic impact on farming lands, leading to devastating food shortages.
Climate Change:
Changes in climate patterns fundamentally affect agriculture. Rainfall patterns, temperature increases, and cyclones have contributed to rising sea levels, causing food crisis and scarcity of fresh water.
To the conclusion of which, each specific individual and organization should take urgent actions to overcome the global food crisis. Furthermore, it is incumbent upon the international community to respond decisively and comprehensively to this crisis in order to promote food security.

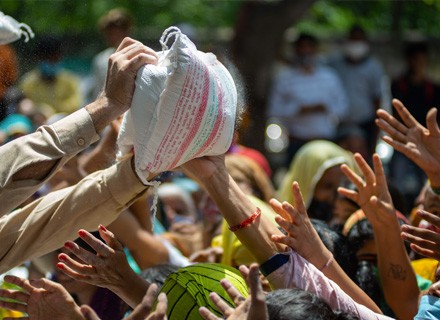





Add comment